What is DomainKeys – DomainKeys is an email authentication technology developed by Yahoo, and is primarily used as an additional anti-spam and anti-phishing method.
How DomainKeys works
- Sending emails
The domain owner generates a public / private key pair to use for signing all outgoing messages (multiple key pairs are allowed). The public key is published in DNS, and the private key is made available to their DomainKey-enabled outbound email servers.
When each email is sent by an account within the domain, the DomainKey-enabled email server automatically uses the stored private key to generate a digital signature of the message. This signature is embedded as a header in the sent email, and the email is sent on to the target recipient’s mail server.
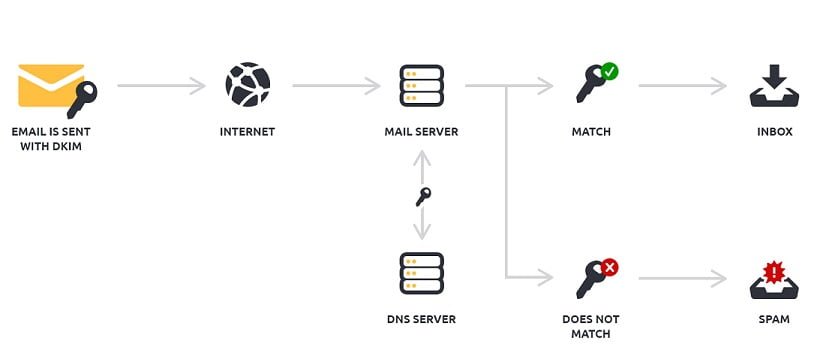
- Receiving emails
The DomainKeys-enabled receiving email server extracts the signature and claimed From: domain from the email headers and fetches the public key from DNS for the claimed From: domain.
The public key from DNS is then used by the receiving mail server to verify that the signature was generated by the matching private key. This proves that the email was indeed sent by, and with the permission of, the claimed sending From: domain and that its headers and content weren’t altered during the transfer.
The receiving email server applies the local policies based on the results of the signature test. If the domain is verified and no other antispam tests catch it, the email can be delivered to the user’s inbox. If the signature fails to verify, or there isn’t one, the email can be dropped, flagged or quarantined.